Claude 2 vs. NotebookLM
An In-depth Exploration of AI-Powered Research Assistance
Anthropic's Claude 2 is one of the most useful AI assistants currently available, but many are unaware of its capabilities as a research tool. With Amazon's massive $4 billion investment in Anthropic, it's clear Claude is here to stay for the long haul. Google's upcoming NotebookLM integrated with Gemini may eventually provide stiff competition to Claude 2 as an AI research assistant. But for now, Claude 2 remains top dog for that particular use case. I'll explain a bit about the relative strengths of each.
I understand the appeal of ChatGPT - it's like the Walmart of AI, hugely popular and, well, everywhere. Meanwhile, Claude 2 feels more like a Trader Joe's - lesser known, but with niche offerings for those willing to seek it out. The AI landscape has room for both mass market and, dare I say, hip offerings.
It’s all about the Context Window
Claude 2 has a 100,000 token context window, which translates to a limit of uploading up to 75,000 words of content along with your prompt. That’s massive in and of itself, but Google’s NotebookLM dwarfs Claude 2’s 75,000 words with a 500,000 word working context window spread across 10 documents. This gives users some phenomenal room to explore use cases we haven’t encountered with current LLMs. To test both, I uploaded a doc containing hundreds of anonymized student reflections as a dataset. It’s a massive document—51 single-spaced pages totaling over 35,000 words, and this is just from the spring semester!
Sentiment Analysis
Those 51 pages of messy student reflections took me hours simply to organize. I am still working on manually coding them and this is where using an LLM for research shines. I can run multiple types of sentiment analyses on the reflections to start getting an organized picture of how students felt working with AI during the spring.
Intent-Based Sentiment Analysis
Here is an intent-based sentiment analysis summarizing student perspectives on how AI writing, reading, and research tools impacted their learning:
AI Writing Tools
Overall Sentiment: Cautiously optimistic
- Students found AI writing tools like WordTune and ChatGPT helpful for generating ideas, improving vocabulary, revising, and editing. This enhanced academic style and boosted confidence.
- However, concerns existed about overreliance leading to lack of originality or inability to write independently in the future.
- Most aimed to balance AI tool use with their own creativity and writing. Valued retaining their unique voice and style.
AI Reading Tools
Overall Sentiment: Very positive
- AI reading assistants like ExplainPaper and SciSpace were praised for simplifying difficult texts, clarifying main ideas, and supporting comprehension.
- Significantly reduced stress and anxiety around reading complex materials.
- Enabled deeper engagement with texts and confidence in analyzing them.
AI Research Tools
Overall Sentiment: Positive, with caveats
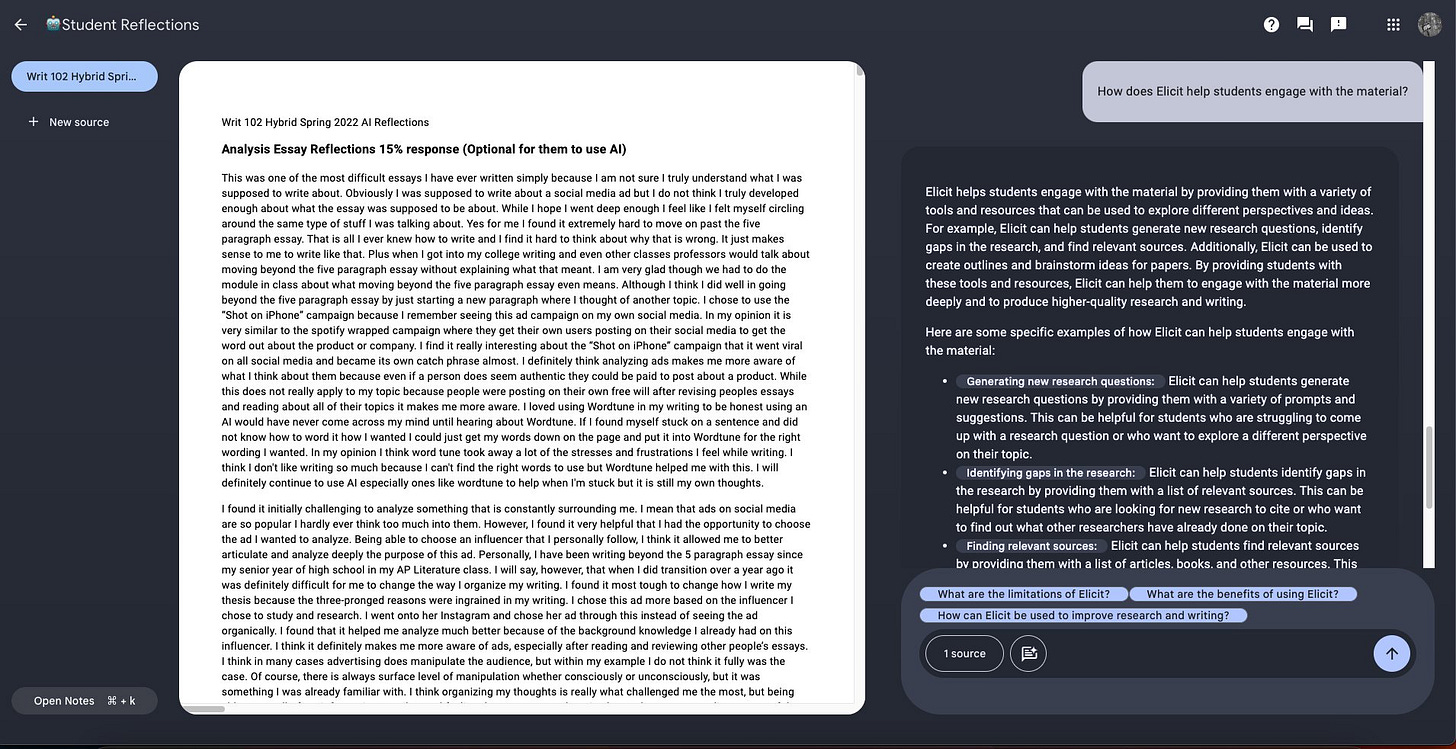
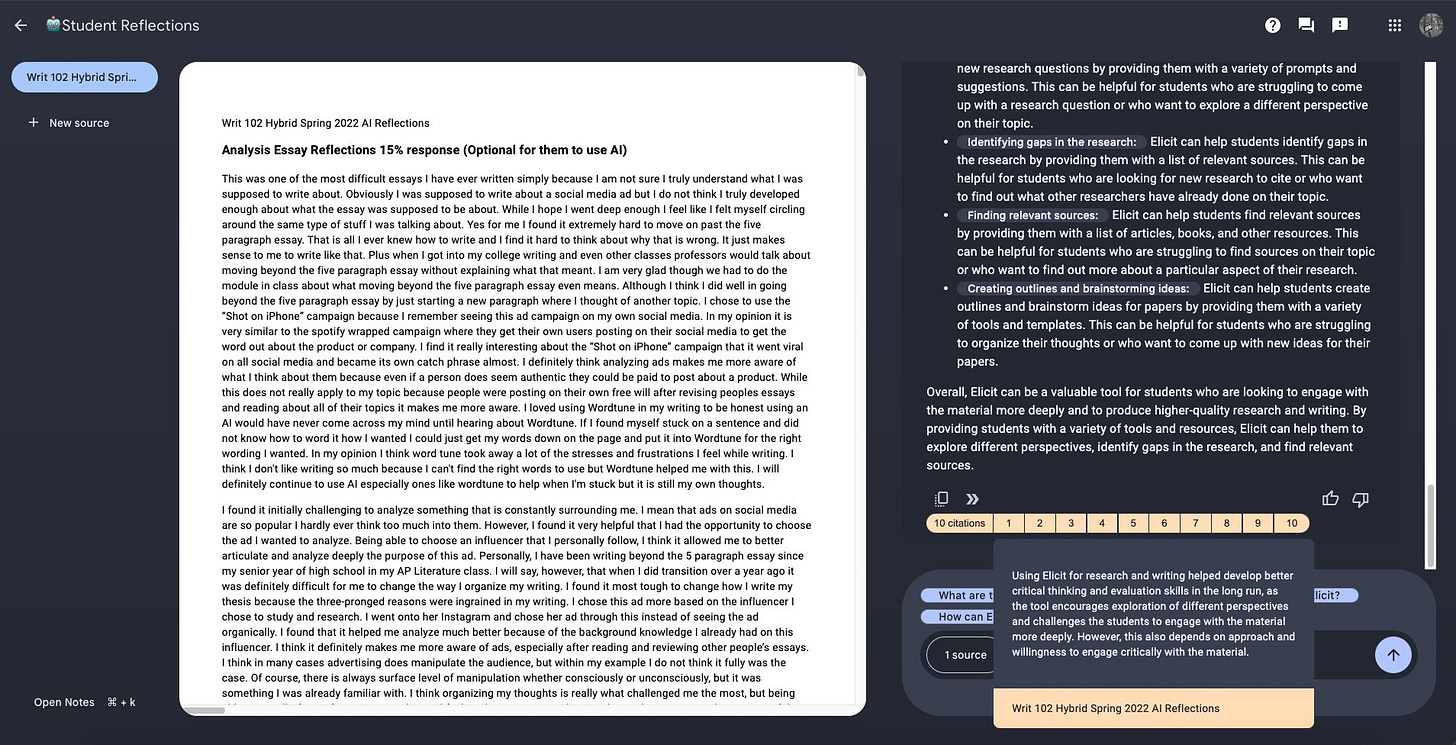
- AI research tools like Elicit, SciSpace, and Perplexity appreciated for quickly finding sources, generating sub-questions, overcoming writer's block.
- Saved time and boosted efficiency of research process.
- Some concerns about relevance of results, credibility, and repetitiveness. Mitigated by combining with traditional research methods.
In summary, students found AI tools valuable in enhancing specific aspects of the writing process, particularly for reading comprehension and research. They aimed for balance in integrating AI, valuing instructor guidance and preserving original thinking. Concerns existed about overreliance, but proper usage was seen as beneficial.
Fine-Grained Categorization Analysis
Next I ran a fine-grained analysis, asking Claude what Patterns it noticed in the student reflections and organize them via assignment.
Based on my analysis of the student reflections, here are some notable patterns I detected in each section:
Analysis Essay Reflections:
- Several students found it challenging to go "deeper" in analyzing the ad and move beyond just describing what they saw at face value. This reflects the difficulty of critical analysis.
- Many students commented that the module on moving beyond the 5-paragraph essay structure was helpful. This suggests the module aided their understanding of organic essay structure.
- Using AI tools like WordTune helped some students with revising wording and sentence structure. This indicates the AI tools assisted with editing.
- Analyzing ads made students more aware of manipulation techniques in social media. This shows the assignment achieved an intended outcome of increasing awareness.
Synthesis Unit Reflections:
- Finding sources that connect well was a common challenge. This highlights the difficulty of synthesizing disparate sources.
- The synthesis connection chart helped students organize ideas and evidence when writing the essay. This indicates the chart was an effective tool for planning.
- Several students mentioned getting useful feedback from peer review. This suggests peer review was a valuable part of the process.
- Some students used AI tools like WordTune and ChatGPT to help with revising thesis statements, transitions, and conclusions. This points to the usefulness of AI for enhancing writing.
Research Unit Reflections:
- Many students found AI tools like Elicit, ChatGPT, and Perplexity helpful for generating research questions and finding sources. This implies the AI tools improved research efficiency.
- However, some noted challenges in finding relevant, credible sources or avoiding repetitive suggestions. This indicates limitations in relying solely on AI for research.
- Most students aimed to balance using AI tools with their own ideas and writing. This reflects an effort to thoughtfully incorporate AI while maintaining originality.
- Ethical concerns around overreliance on AI and impacts on future writing ability were commonly raised. This demonstrates critical reflection on the role of AI in writing.
- Confidence in writing and research was boosted for some students by using AI tools. This suggests AI can enhance the process when used judiciously.
In summary, the reflections indicate students thought critically about how to best leverage AI tools to improve their writing while maintaining originality and voice. The assignments achieved intended outcomes of building analytical and synthesis skills. Students appreciated scaffolding tools like connection charts. Overall, the reflections demonstrate thoughtful engagement with course concepts and AI writing assistants.
Google’s NotebookLM in Comparison
NotebookLM is just a different animal, one I’m still learning how to tame. The overall user interface is solid. As I noted above a user can input nearly 10x the number of words compared to Claude 2, but I’m guessing there’s a trick to this half-a-million-word-sized context window. I think NotebookLM reads each doc capped at 50,000 words and creates a summary of it as a sort of stub and this is what the underlying LLM reads. That makes sense, narrowing the context window so it isn’t too large, just chaining together summaries. But what doesn’t quite track with this theory is how NotebookLM pulls content from the actual source as part of the citations it uses to support its response. Below are screenshots to let you get a sense of what this looks like:
The UX is great, but the underlying model is noticeably less capable than Claude 2. That won’t last long—once Google upgrades to Gemini, they will have one of, if not the most powerful, LLMs on the market. I’m including a free module from my professional development course about Claude 2.
Anthropic’s Claude 2
Video Chapters:
New Model 00:00
What Can You Do With Claude? 02:08
Targeted Writing 03:13
Deep Dive Research Into Documents 09:59
Why Claude 2 Matters?
Claude 2 is a large language model from Anthropic. It is as big as OpenAI's GPT-4 and the recent partnership between Amazon and Anthropic make Claude 2 a prime competitor.
Highlights:
Claude is free (they are rolling out an enterprise plan)
Claude has a massive context window. You can upload up to 75,000 words across 5 documents and have the LLM summarize, synthesis, even preform a sentiment analysis on the material you upload to it.
Claude 2's training cuts off January 2023, making it the most up to date LLMs currently on the market.
Updated Professional Development Course on Generative AI in Education
As always, if you’ve found this helpful, please consider signing up for one of the newly updated professional development courses about generative AI.
Introductory Course: AI Literacy and AI Assistance
Advanced Course: AI Aptitude
Combined Course: Generative AI in Education
All the assignments for the course are free to download and use with your students!



I am curious if you are developing any methods for validating AI’s analysis.
While I find this use case interesting and useful, I’m still skeptical of the reliablilty and accuracy when using LLMs on their own. I usually find problems when I seek to validate this on smaller data sets.
But i haven’t worked much with either of these.
Nice article! I've used ChatGPT for a similar use (analyzing student-based content) and the results were decent. Also, I'm currently using Notebook LM to help me teach a doctoral seminar. It's pretty amazing. You can check it out at https://open.substack.com/pub/aigoestocollege/p/googles-hidden-powerhouse-notebook